Eye-related conditions can be concerning and uncomfortable, and two common conditions that can affect the eyelids are blepharitis and stye. Although these conditions share some similarities yet they have distinct characteristics and require different treatment approaches.
Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the eyelids. It involves the inflammation of the eyelid margins where the eyelashes are located. This condition can be caused by various factors that include bacterial infections, skin conditions and dysfunction of the oil glands in the eyelids.
Causes of Blepharitis
The causes of blepharitis can include:
- Bacterial Infections: Bacteria such as staphylococcal or seborrheic bacteria can colonize the eyelid margins and contribute to the development of blepharitis.
- Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions such as rosacea or seborrheic dermatitis can affect the eyelids and lead to blepharitis.
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Dysfunction of the meibomian glands which are responsible for producing the oily layer of tears can cause blepharitis. When these glands do not secrete enough oil or if the oil becomes thick and clogs the glands it can lead to inflammation.
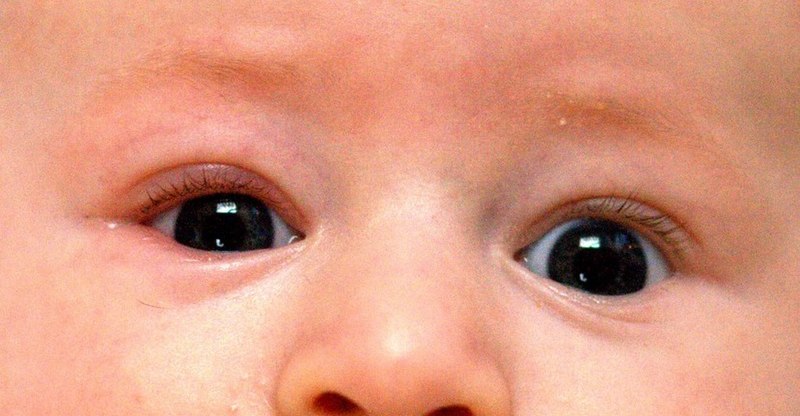
Symptoms of Blepharitis
The symptoms of blepharitis can vary but commonly include:
- Eyelid Redness and Swelling: The eyelids may appear red and swollen particularly along the eyelid margins.
- Eyelid Itching and Irritation: Blepharitis can cause itching, burning or a sensation of foreign body presence in the eyes.
- Crusty or Sticky Eyelids: The base of the eyelashes may become crusty or sticky especially upon waking up in the morning.
- Watery or Dry Eyes: Some individuals with blepharitis may experience excessive tearing while others may experience dryness and discomfort.
Treatment of Blepharitis
The treatment of blepharitis aims to manage the symptoms and control the underlying causes. Some common treatment options include:
- Eyelid Hygiene: Regular eyelid hygiene is crucial in managing blepharitis. This may involve gently washing the eyelids with warm water and using a clean, warm washcloth to remove any crusts or debris.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyes can help loosen the oil in the meibomian glands promoting better tear quality and reducing inflammation.
- Eyelid Scrubs: Your eye care provider may recommend using a mild eyelid scrub or cleanser to remove excess oil, debris and bacteria from the eyelids.
- Medicated Eyelid Solutions: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe medicated eyelid solutions or ointments to control bacterial growth and inflammation.
Stye (Hordeolum)
A stye, also known as hordeolum is a common eyelid infection that affects the base of the eyelashes or the oil glands within the eyelids. It appears as a red, painful lump on the eyelid and can be caused by bacterial infection.
Causes of Stye
The main cause of a stye is a bacterial infection usually by staphylococcal bacteria. The infection can occur when bacteria enter the oil glands or hair follicles on the eyelid leading to inflammation and the formation of a stye.
Symptoms of Stye
The symptoms of a stye may include:
- Red, Tender Lump: A stye typically appears as a red, swollen and painful lump on the eyelid, resembling a pimple or boil.
- Eyelid Swelling: The affected eyelid may become swollen and tender to the touch.
- Eyelid Pain and Discomfort: Stye can cause discomfort especially when blinking or applying pressure to the affected area.
- Crusting of the Eyelashes: The base of the eyelashes near the stye may develop crusts or debris.
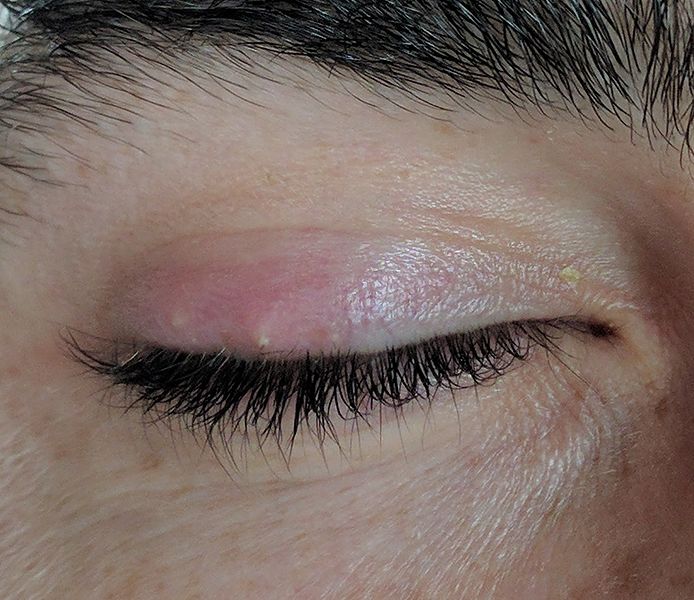
Treatment of Stye
Most stye resolve on their own within a few days to a week. However, some measures can be taken to alleviate symptoms and promote healing:
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the affected eyelid can help reduce inflammation, increase blood circulation and promote the drainage of the stye.
- Avoid Squeezing or Popping: It is important to resist the temptation to squeeze or pop the stye as this can spread the infection and potentially lead to complications.
- Good Hygiene: Practicing good eyelid hygiene such as washing your hands before touching your eyes and avoiding the use of eye makeup during a stye can help prevent further infection.
- Antibiotic Ointments: In some cases, your doctor may prescribe antibiotic ointments to apply to the stye to help clear the infection.
While both blepharitis and stye can affect the eyelids, they are distinct conditions with different causes and treatments. Blepharitis is a chronic inflammatory condition that involves the eyelid margins and can be caused by bacterial infections, skin conditions or meibomian gland dysfunction. On the other hand, a stye is an acute infection of the eyelid caused by bacteria. Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for proper diagnosis and appropriate management.